How to set up NTRIP caster on a remote Ubuntu server
-
Introduction
YCCaster is a multi platform NTRIP caster designed to work as part of modern web applications. In this tutorial, we’ll discuss how to install YCCaster on your Ubuntu 20.04 server, adjust the firewall, configure access rights for bases and rovers, and set up monitoring.
Initial server setup
First of all, we need a virtual server on Ubuntu 20.04. Since our caster is quite lightweight, a minimal Linux server from Linode or DigitalOcean will work. I recommend these hosting providers for their newbie friendliness and reasonable pricing.
For the purposes of this tutorial, I will be using a virtual server from Linode. If you do not have an account, you need to register. Then log into your account and create a new server.
Installation.
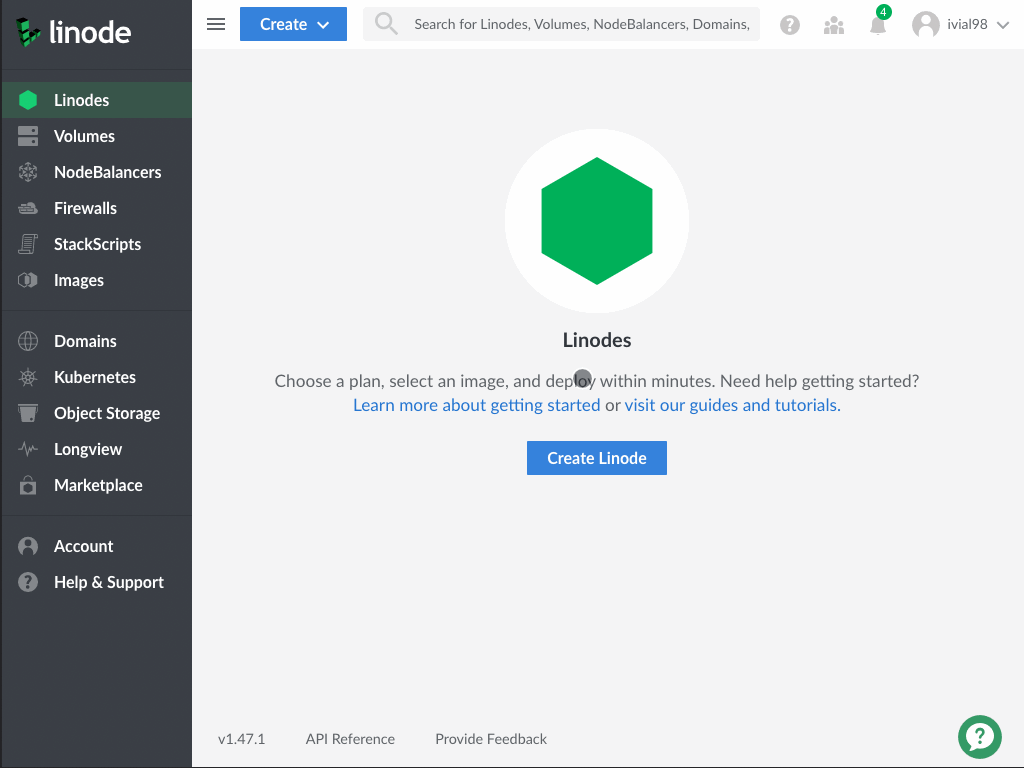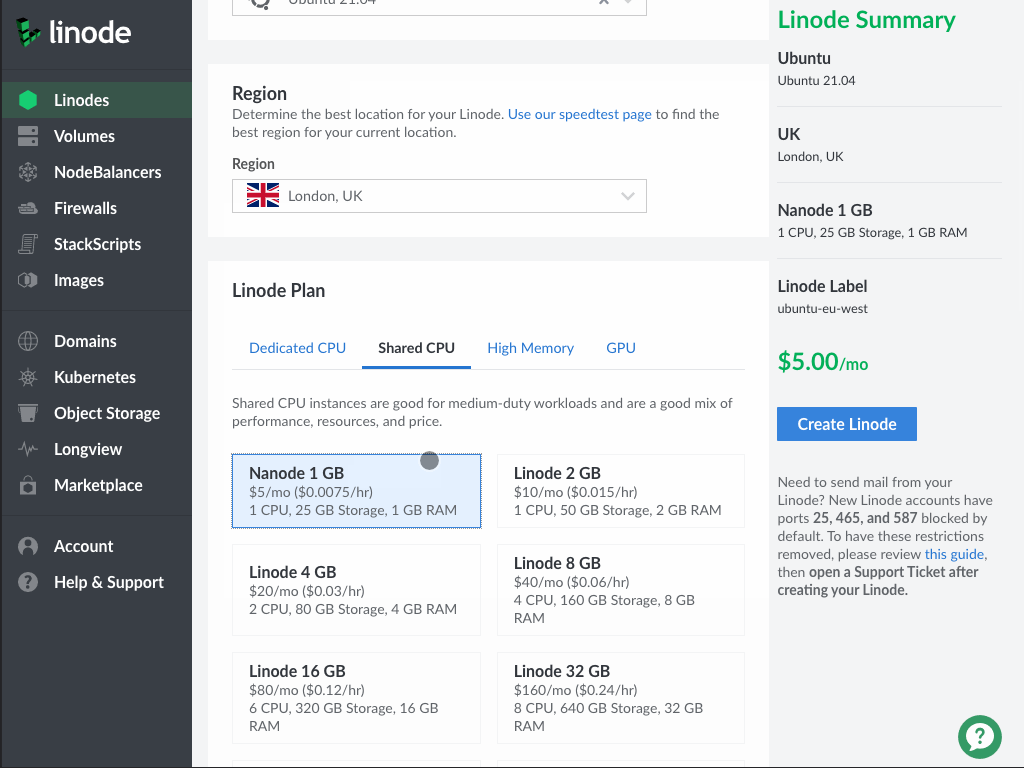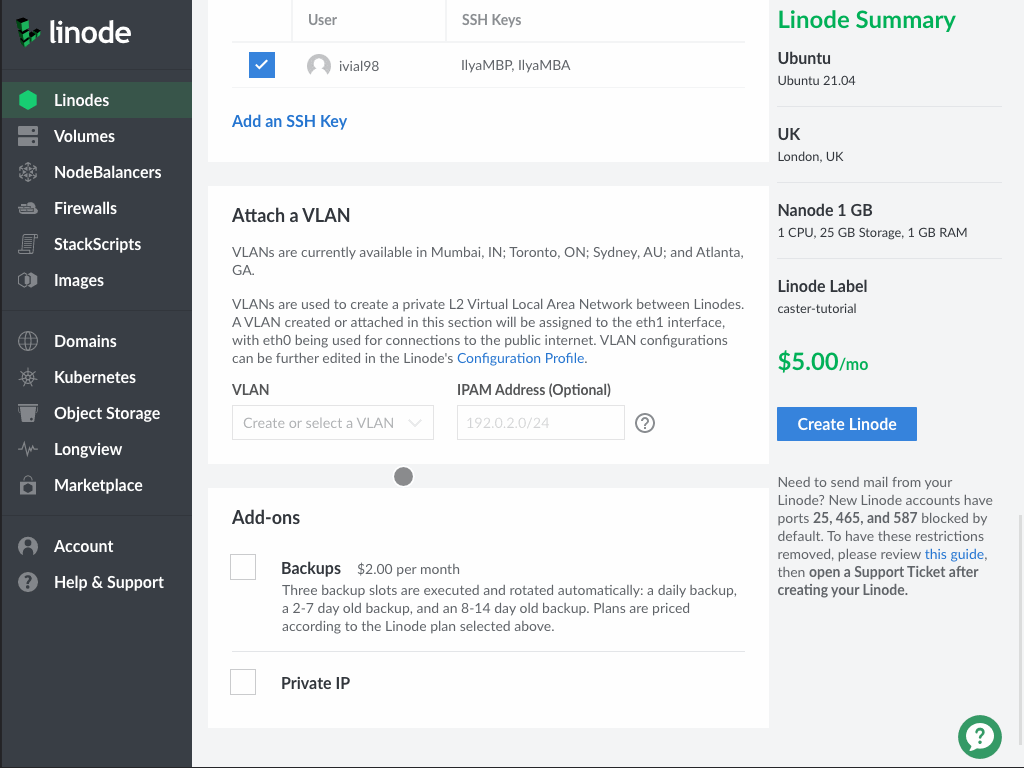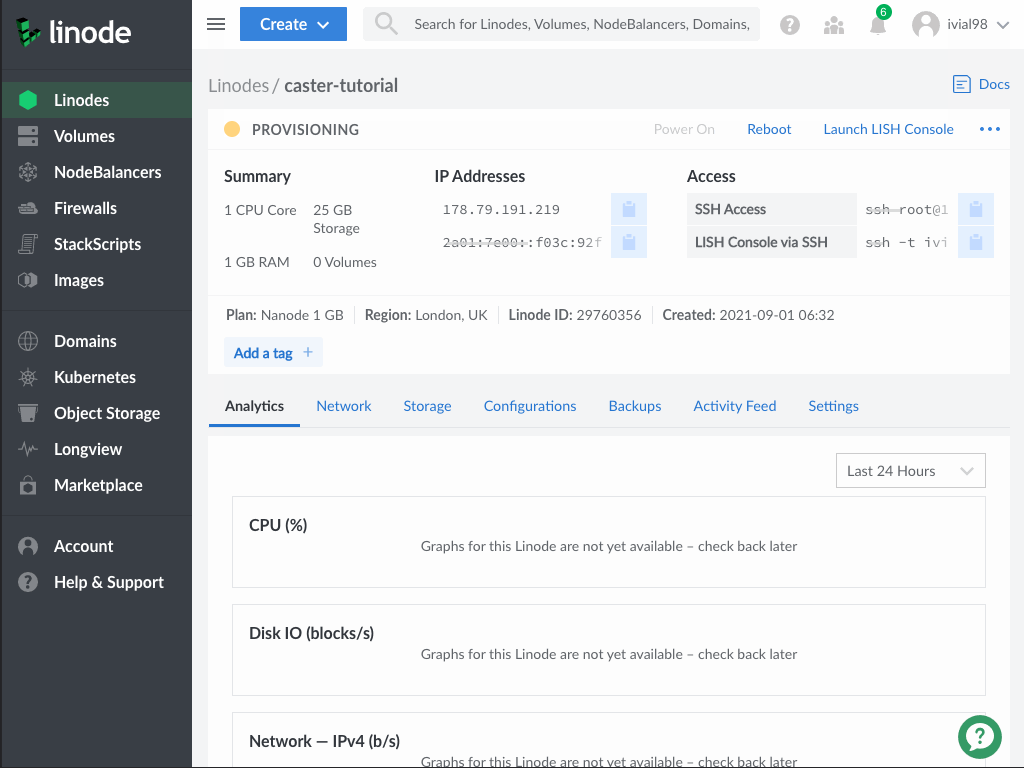
To install the caster, we need to establish an ssh connection to our server. The easiest option is to use the Linode LISH console, the terminal will open in a new browser window. If you are using Linux or MacOS, open your terminal and establish an ssh connection. To log in, you will need the password that was set when creating the server.
ssh root@178.79.191.219For security reasons, it is better to run caster with non root user permissions. For this we will create a separate user.
useradd casterThen download caster from YCCaster website to a new folder and make it executable.
mkdir -p /var/caster && wget https://yccaster.s3.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com/bin/1.0.1/linux-amd64/yccaster -O /var/caster/yccaster && chmod +x /var/caster/yccasterGenerate initial config file.
cd /var/caster && ./yccaster initNow we are ready to launch the caster but to work in the background it needs a linux service that will launch the caster if the server restarted or if the caster crashed. To create the service, execute this command.
cat << EOF > /etc/systemd/system/caster.service [Unit] Description=YCCaster Requires=network-online.target After=network-online.target [Service] Type=simple User=caster Group=caster Restart=always RestartSec=10 WorkingDirectory=/var/caster ExecStart=/var/caster/yccaster StandardOutput=append:/var/log/caster.log StandardError=append:/var/log/caster.log [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOFThen enable caster service.
systemctl enable caster.serviceAnd start caster
systemctl start caster.serviceNow the caster is up and running. To check it, you can use this command.
systemctl status caster.serviceIt should display active status
root@localhost:/var/caster# systemctl status caster.service ● caster.service - YCCaster Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/caster.service; enabled; vendor preset> Active: active (running) since Thu 2021-09-02 05:41:54 UTC; 8s ago Main PID: 16298 (yccaster) Tasks: 5 (limit: 1040) Memory: 1.5M CGroup: /system.slice/caster.service └─16298 /var/caster/yccaster Sep 02 05:41:54 localhost systemd[1]: Started YCCaster. lines 1-10/10 (END)Testing
Now when the caster is running we can test it and establish a connection between base and rover. To emulate base and rover I will use YCServer. It is an NTRIP server and client application for Android. You can download it from the play market.
I will use two instances of YCServer (probably, you will need two phones to run them simultaneously).
First instance will generate fake data and act as a base station. Second instance will act as a rover, receive data from the caster and save it to file.
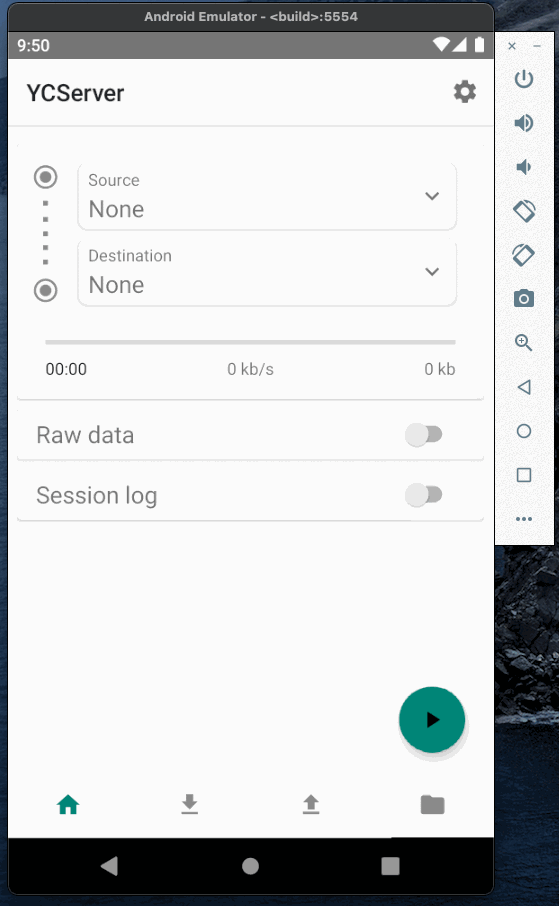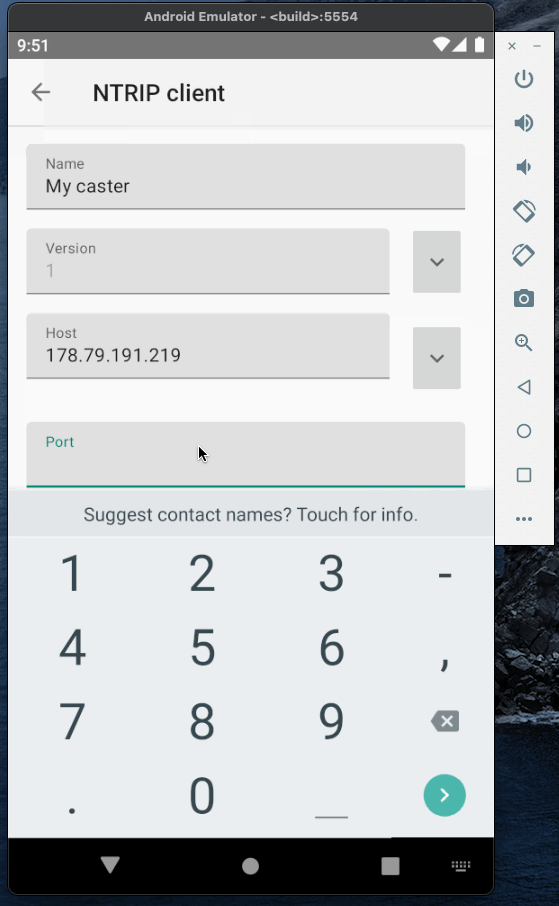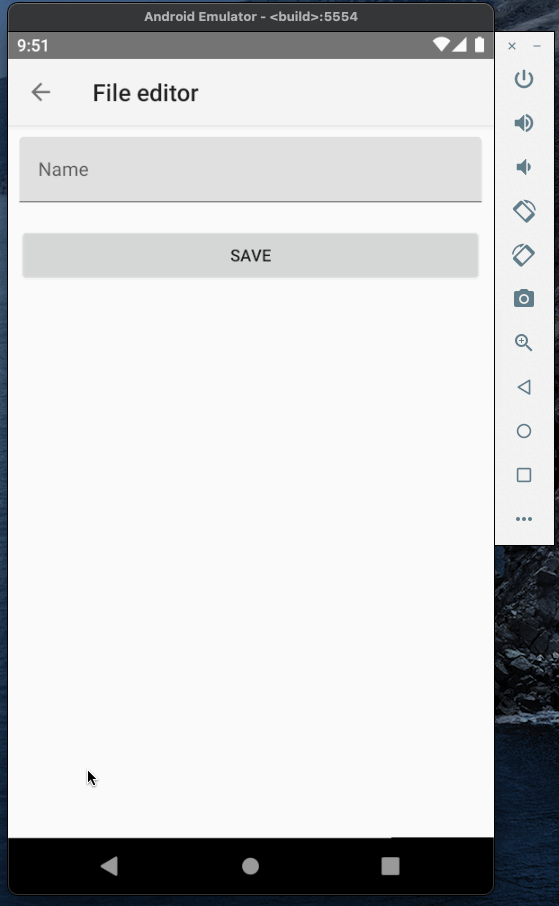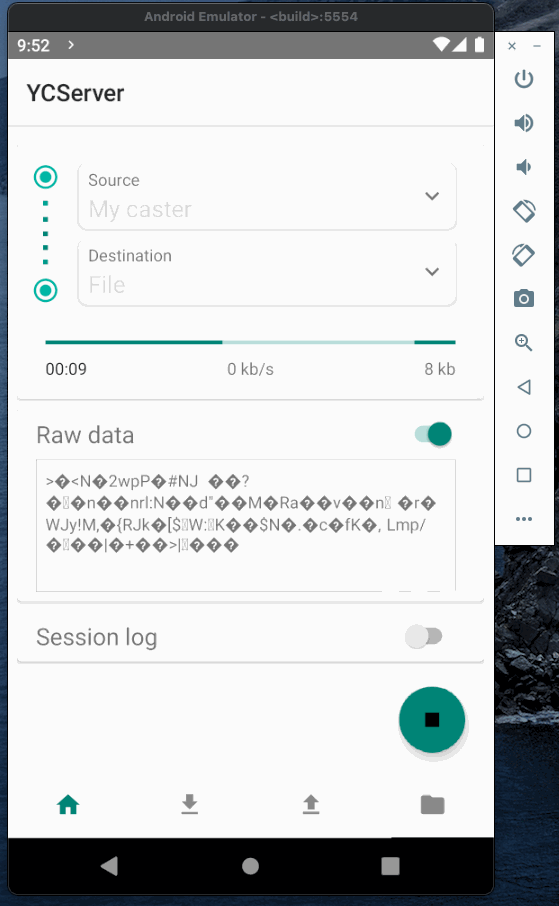
Base and rover Authorization
The caster that we launched does not check passwords for connecting bases and rovers. Everyone can connect to it and transmit and receive data. If we need to restrict access and allow only authorized clients to exchange data, we need to change the configuration file and add the following section to it:
configuration: auth: - type: file options: mount-points: mountpoints.yml clients: clients.ymlIn this section, we stated that authorization will be based on files and that the
mountpoints.yml file will be used to authorize base stations and clients.yml for roversCreate a new mountpoints.yml file in the same directory as the configuration file.
- mount-point: NICOSIARTKBASE password: 12345 description: identifier: Nicosia format: RTCM 3.2 format-details: 1006(15),1008(15),1013(60),1019,1020,1033(15),1075(1) carrier: 2 nav-system: GPS+GLO+GAL network: EUREF country: CYP latitude: 35.15 longitude: 33.37 nmea: 0 solution: 0 generator: u-blox zed-f9p compr-encryp: none authentication: B fee: N bitrate: 6200 misc: Nicosia district base - mount-point: PAPHOSRTKBASE password: 678910 description: identifier: Paphos format: RTCM 3.2 format-details: 1006(15),1008(15),1013(60),1019,1020,1033(15),1075(1) carrier: 2 nav-system: GPS+GLO+GAL network: EUREF country: CYP latitude: 34.77 longitude: 32.41 nmea: 0 solution: 0 generator: u-blox zed-f9p compr-encryp: none authentication: B fee: N bitrate: 6200 misc: Paphos district baseIn this file, we have specified 2 mount points. In addition to the name and password, you can specify a description of the stream, which will be used to generate the NTRIP SOURCETABLE.
Next, let's create the clients.yml file in the same directory.
- username: firstrover password: 12345 - username: secondrover password: 12345 - username: thirdrover password: 12345In it, I indicated the names of 3 rovers and their passwords.
In order for the changes to take effect, you need to restart the caster.
systemctl restart caster.serviceNow only the base stations and rovers listed in the corresponding files will have access to the caster.